Is a Recession Coming? What It Means for the Housing & Mortgage Market in 2025
Updated Wed, Mar 12, 2025 - 7 min read
If you’ve been watching the economy lately, you might be wondering: Are we heading toward a recession? With rising consumer debt, ongoing trade tensions, and inflation a lingering concern, there’s a lot of uncertainty in the air. For homebuyers, sellers, and real estate investors, understanding what’s happening in the broader economy is crucial—especially when it comes to mortgage rates and housing prices.
Let’s break down the current recession risk and how it could impact the mortgage market in 2025.
Recession Watch: Are the Warning Signs Flashing?
Economists and investors are paying close attention to several key indicators that suggest the U.S. economy could be slowing down. Here are a few of the biggest red flags:
1. Trade Wars Are Back
Recent tariffs imposed by the U.S. on China, Mexico, and Canada have rattled global markets. These tariffs, combined with rising import costs, have made businesses nervous, leading to lower hiring rates and potential layoffs. Economic uncertainty like this often triggers a slowdown in consumer spending—one of the main drivers of growth.
Here is an outline of the tariffs Trump has implemented so far.
Tariffs on Canada and Mexico
On March 3, 2025, President Trump imposed a 25% tariff on all imports from Canada and Mexico, citing concerns over illegal immigration and drug trafficking. These tariffs affect automobiles, agriculture, and raw materials, driving up costs for manufacturers and consumers. Both Canada and Mexico retaliated with tariffs on U.S. goods, including dairy, auto parts, and industrial equipment.
Let's connect, and see how we can help you stay ahead of the market.
Contact us
Tariffs on the European Union
On February 26, 2025, the administration introduced 25% tariffs on all EU imports, targeting industries like automobiles, luxury goods, and aircraft manufacturing. European automakers, including Volkswagen and BMW, have been hit hardest, while the EU responded with tariffs on U.S. whiskey, motorcycles, and agricultural products.
Tariffs on China
On February 4, 2025, the U.S. implemented 10% tariffs on all Chinese imports, which were increased to 20% on March 4. In response, China imposed tariffs on U.S. energy, agricultural goods, and high-tech exports, while launching regulatory investigations into U.S. firms. The trade war has further strained global supply chains and intensified recession fears.
Economic Impact
The tariffs have driven up inflation, disrupted supply chains, and led to increased market volatility. Major stock indices have declined, while mortgage rates remain uncertain, as the Federal Reserve weighs recession risks. Economists warn that these tariffs could slow GDP growth and further strain consumer spending.
Stock Market Response
The announcement and subsequent implementation of these tariffs have led to heightened volatility in the stock markets:
- Major Indices Decline: The Dow Jones Industrial Average experienced a significant drop, plunging over 1,000 points in a single day. Similarly, the Nasdaq Composite Index entered correction territory, declining by more than 10% from its recent highs.
- Market Volatility: The VIX index, which measures implied volatility in the S&P 500, has risen to its highest level since the Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts in December. This spike indicates increased uncertainty among investors. reuters.com
- Sector-Specific Impacts: Companies heavily reliant on international trade, such as major exporters and manufacturers, have been particularly affected. For instance, Tesla’s shares plummeted by 15%, marking a 50% decline from its all-time high in December. The Guardian
- Growth Projections: Goldman Sachs revised its economic growth forecast for 2025 from 2.4% to 1.7%, citing the potential negative impacts of the ongoing trade disputes. CBS News
2. Bond Market Signals Trouble
One of the most reliable predictors of a recession is the yield curve inversion—which happens when short-term interest rates are higher than long-term rates. It’s a sign that investors are worried about future growth; investors are fleeing into the safety of long-term bonds, pushing down their yields. While not every yield curve inversion leads to a recession, it has been one of the most reliable early warning signs, appearing before every major downturn in the past 50 years. The yield curve was inverted for two years spanning late 2022 through December of 2024. It uninverted in early 2025 but has recently reinverted again.
3. Consumer Debt is Climbing
Americans are carrying more debt than ever, especially on credit cards. The average household is now juggling over $10,000 in credit card debt, and delinquency rates are creeping up. If the job market weakens, many people may struggle to keep up with their mortgage payments, which could lead to higher foreclosure rates and a cooling housing market. If interest rates remain high, this debt load may be difficult for consumers to pay off—leading to reduced consumer demand.
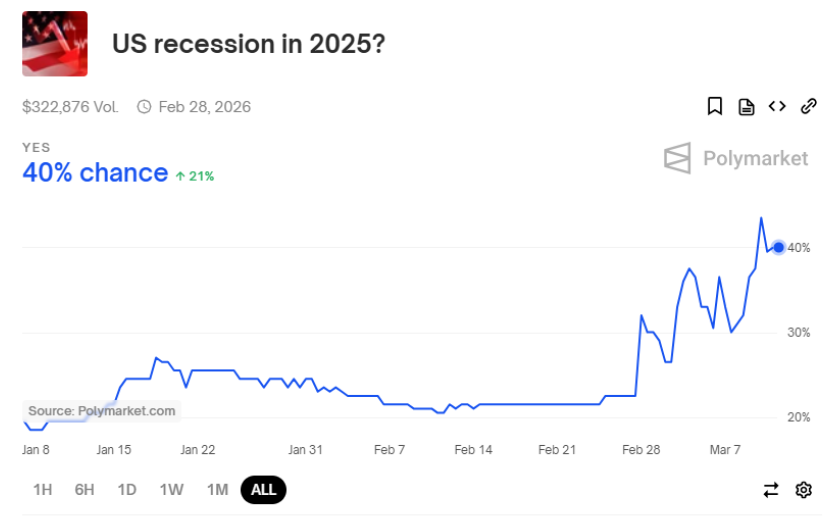
4. Prediction Markets have seen a sharp rise in the probability of a recession
Polymarket is a prediction market where users buy and sell shares in future events, with prices between $0 and $1 reflecting the probability of an outcome. If “U.S. recession in 2025” is trading at $0.40, the market believes there’s a 40% chance of a recession. The rise in this probability from just above 20% to 40% signals increasing investor concern. Recently, Trump’s trade war tariffs and stock market volatility have pushed recession odds higher, indicating that traders expect worsening economic conditions.
How Could This Impact Mortgage Rates?
If the economy slows down, the Federal Reserve may cut interest rates to prevent a full-blown recession. That could lead to lower mortgage rates, making it cheaper for buyers to borrow money. That said, the inflationary pressures created by tariffs could lead to rates remaining elevated prior to the downturn.
Right now, mortgage rates have come down slightly, with the average 30-year fixed rate hovering around 6.63% (down from 7% earlier this year). However, if recession fears grow, we could see rates dip even further—potentially creating opportunities for buyers who have been sitting on the sidelines.
On the flip side, lenders may tighten their lending standards if a downturn becomes more likely. That means getting approved for a mortgage could become harder, especially for borrowers with lower credit scores or smaller down payments.
Will Home Prices Drop in 2025?
That’s the big question on every buyer’s mind. If a recession does hit, it won’t necessarily lead to a housing crash like we saw in 2008. Today’s market is still dealing with low housing inventory, which could keep prices from falling too dramatically.
However, home sales have already slowed, and if recession fears continue to grow, sellers may be forced to lower prices to attract buyers. We’re already seeing an increase in price reductions in certain markets, particularly in high-cost areas where affordability is a challenge.
What Should Buyers & Homeowners Do Now?
📉 If you’re a buyer: Keep an eye on mortgage rates and be ready to move if they drop further. But don’t overextend yourself financially—make sure your budget can handle potential job market fluctuations.
If you’re a seller: Price Strategically: With home sales slowing, overpriced listings may sit on the market longer. Consider pricing competitively to attract serious buyers. Consider selling sooner: Ask yourself if you could last through a recession. Of course, because a recession will reduce interest rates, it may not put as much negative pressure on home prices as one would expect. If the recession hits certain sectors harder than others, different parts of the country might experience different levels of price decline—with some even continuing to see increases.
If you’re a homeowner: If you’ve been thinking about refinancing, you might get the opportunity in the near future. Homeowners should keep in mind that lenders will tighten their requirements as recession risk increases.
Final Thoughts
While no one can predict the future with absolute certainty, recession risks are rising, and that’s something everyone in the housing market should pay attention to. Whether you’re looking to buy, sell, or refinance, staying informed and prepared is key.